Are you an aspiring agribusiness entrepreneur seeking to capitalize on Kenya’s booming food industry? Look no further! Discover the latest trends and data on Kenya’s agriculture scene and how it can be used to transform your business operations. With data being hailed as the new gold, you don’t want to miss out on the rich insights provided by this analysis.
You will learn about livestock populations, the most popular crops and land use, this report has it all. Gain a competitive edge by understanding the future food demand and supply trends and unlock profitable agribusiness opportunities. Well used, this will likely take your agribusiness to the next level!
Read Also: 2019 census Data; Exploring best Agribusiness Opportunities
The KPHC 2019 census results have insights for all agricultural players. This analysis will focus on three priority areas. Country’s agriculture activities. human population and urbanization.
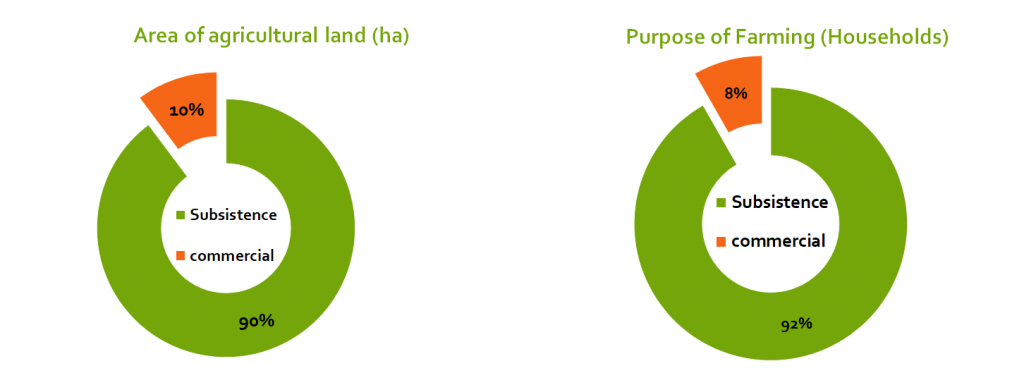
Less than 10% of Kenyans engage in commercial farming
The main purpose of farming in Kenya is subsistence. 5.6 Million households out of 6.3 million households, farm for food production. In relation to land use, a total of 8.43 million hectares out of 10.03 million arable land are is under subsistence production.
According to studies, the small farmers in Kenya produce over 70% of marketed farm products. They farm in small land parcels of less than 2 acres which cannot support mechanization. Land’s productivity in Kenya is also fast declining.
A Breakdown of the Kenya’s Livestock Populations
You won’t believe which livestock is the least popular in Kenya! Is it time to reconsider pig farming for profitable agribusiness?
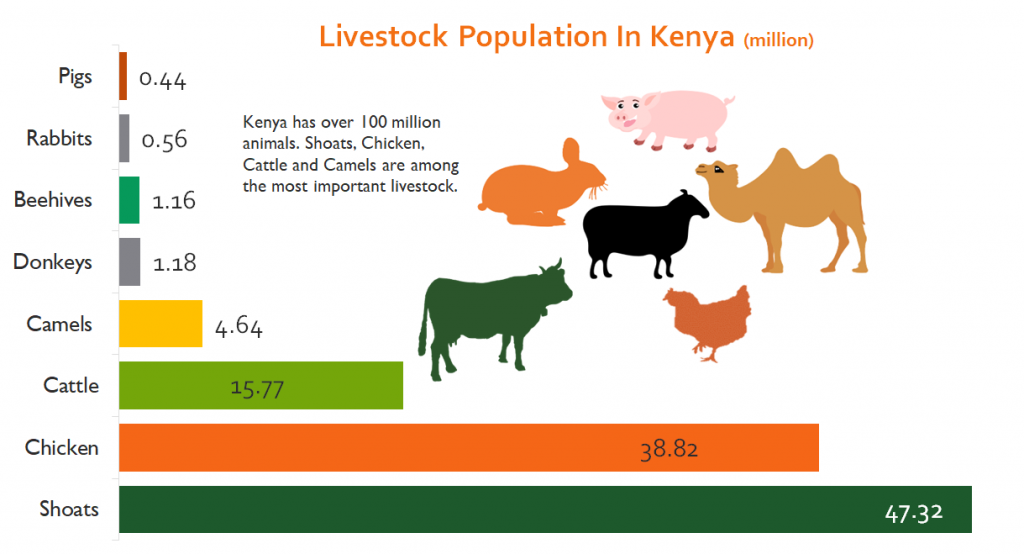
A Breakdown of the Country’s Livestock Populations is as follows!” Kenya’s livestock populations according to the 2019 census results include;
- 38.8 million chicken birds
- 47.3 million sheep ad goats
- 15.7 million cattle. There
- 4.6 million camels,
- 1.2 million donkeys
- Rabbits and pigs are 0.5 million and 0.4 million respectively.
- 1.16 million beehives in the country.
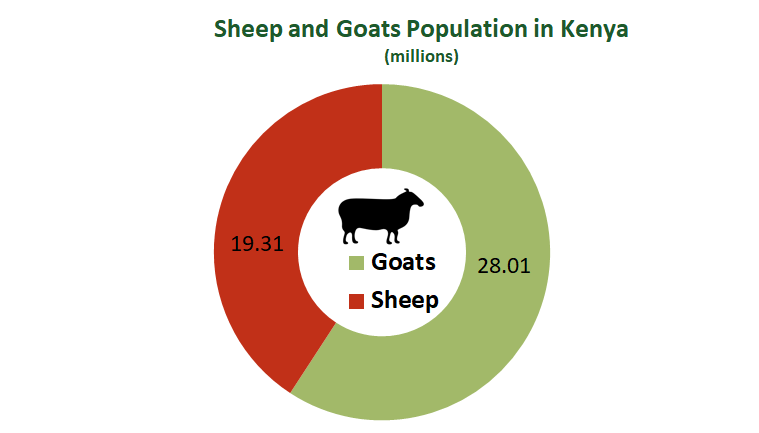
47M Small Ruminants
Did you know that small ruminants reign supreme in Kenya’s livestock industry? With 47.32 million animals across the country, goats are the preferred choice over sheep farming, with 28.01 million and 19.31 million respectively. Tap into this thriving market and discover why small ruminants could be your next profitable agribusiness venture.
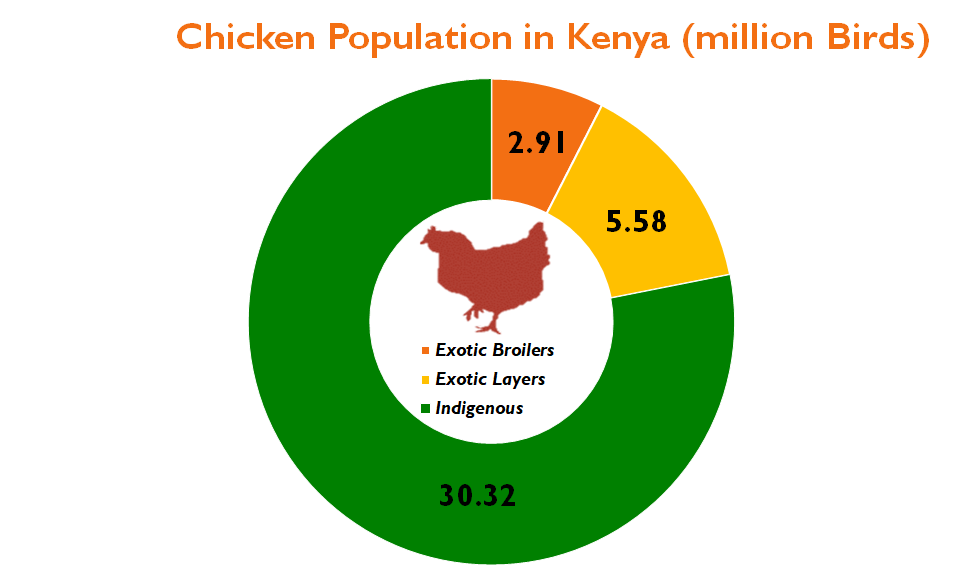
30 M Indigenous chicken
Did you know that Kenya is home to 38.82 million chickens, with indigenous breeds making up the majority at 30.32 million birds? Join the poultry farming revolution and discover the lucrative opportunities for commercial chicken farming, including the rising demand for exotic layers. Don’t miss out on your chance to hatch a successful agribusiness venture in Kenya’s thriving poultry industry!
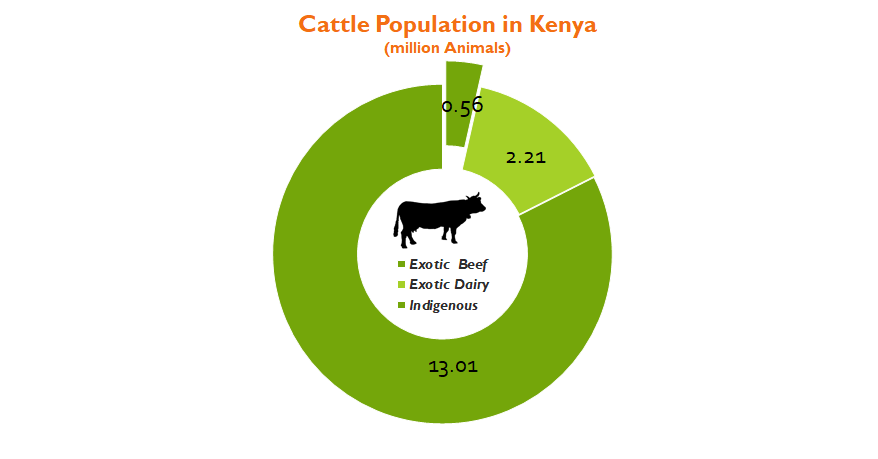
13M Indigenous Cows
The most profitable cattle farming in Kenya is Pastoral beef farming. According to the 2019 census results, Kenya has 13.01 million indigenous cows are owned by herder communities in the ASAL regions. There were 2.21 exotic dairy cattle that are concentrated in the central highland areas for milk production. Ranchers concentrate on exotic beef cattle which were 0.56 million during the study.
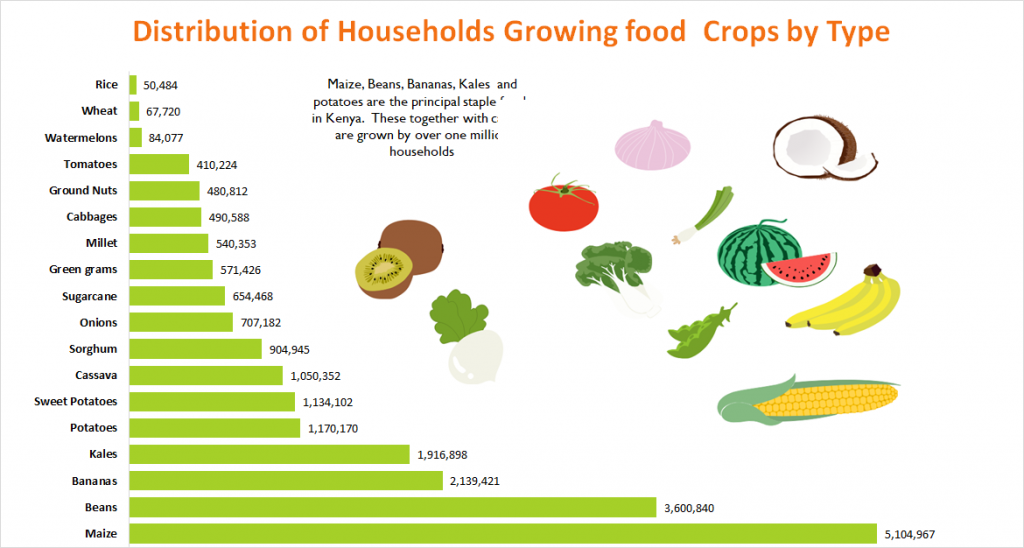
Obsessional maize farming
The analysis analyzed the number of households growing food crops like maize, beans and bananas. The other area that was analyzed is distribution of farming households engaged in commercial crop farming. These grew permanent cash crops like tea, coffee and miraa. other emerging cash crops that were in the report are the fruit trees like avocado, mango and macadamia.
Maize and beans are the favorite food crops in Kenya. Out of 5.6 million households that report practicing crop farming, 91 per cent grow maize. 64 per cent of the households grow beans. Other popular food crops grown by most farming households are bananas, kales, cassava and sweet potatoes. The crops with the least farmers in Kenya are rice and wheat.
This information proves there is a need for investment in research and promotion towards the adoption of alternative and orphan crops such as pulses, sorghum, millet, cowpeas and green grams in vast semi-arid regions. This will be a measure of diversifying our national food basket.
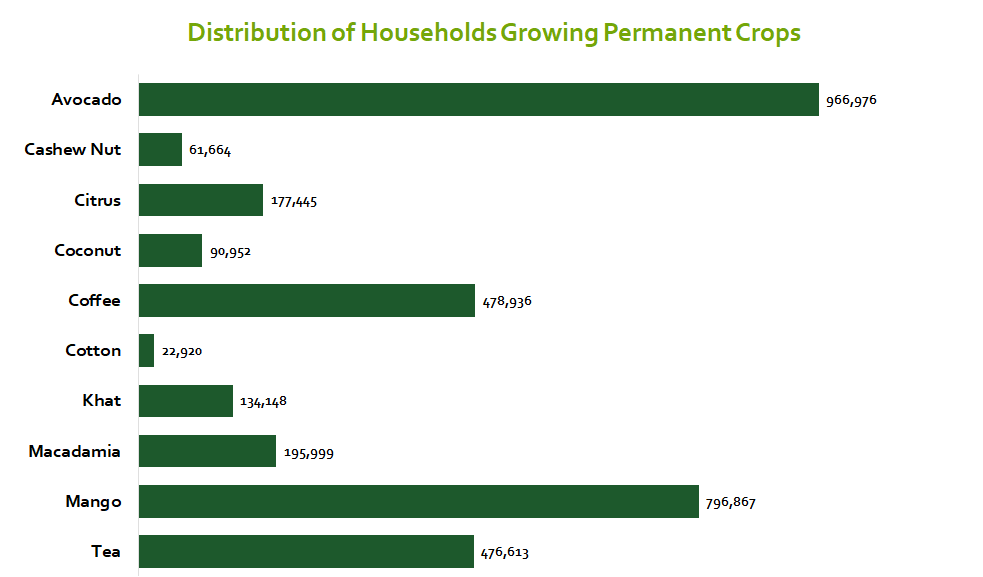
Avocado Farming is the most popular permanent cash crop in Kenya
Avocado and mango trees are the most popular permanent crops grown in Kenya. They are farmed by 0.96 Million and 0.79 million households respectively. This is far higher compared to tea, coffee and cotton growers. There is a need for investments to improve our domestic capacity to process our fruits. This will reduce the incidences of post-harvest food losses, especially when all trees have matured and actively producing. Avocadoes can literally lift a million farmers from poverty.
Only O.37 million farmers do irrigation farming
Kenya’s hunger Crisis can be explained by numbers. There are Only 370,000 Farmers Practicing Irrigation. With devastating droughts occurring every 10 years, rain-fed crop production is no longer a sustainable solution. The time to act is now: let’s come together and promote climate-smart agriculture by embracing irrigation and fast-maturing crops.
Less than 2% of Kenyans have a kitchen garden
There is Shocking Truth About Urban Farming in Nairobi and Kenya at large: Only 0.032M Households Participate Despite Rapid Urbanization. With the looming threat of food insecurity, it’s time for city dwellers to wake up and take action. Imagine harvesting fresh fruits, milk, eggs, and meat right from your backyard, balcony, or rooftop – the benefits are clear, yet adoption rates remain alarmingly low. Let’s take charge of our own food supply and embrace the power of urban farming today!
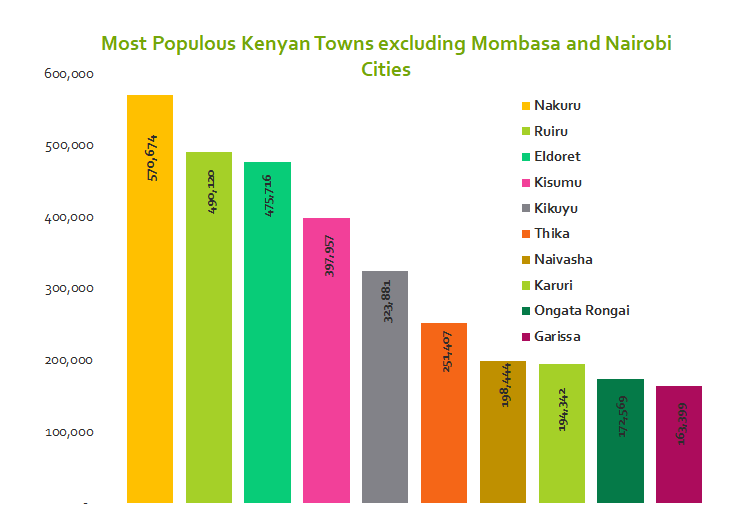
30.8 per cent (14.7 million people) of Kenyans live in towns according to the 2019 census by KNBS. The country’s capital, Nairobi, is the most populous with 4.3 million people. The coastal historical city of Mombasa is second with 1.2 million people. The top ten most populous towns excluding the above cities are Nakuru, Ruiru, Eldoret, Kisumu, Kikuyu, Thika, Naivasha, Karuri, Ongata Rongai and Garissa.
This presents two unique challenges;
- shrinking farmlands as we set up residential flats on fertile areas.
- An older population of farmers in rural areas whose average age is around 60 years as rural-urban migration continues.
Kenya’s food insecurity is worsening
Kenya has a total population of 47.6 million people. This has increased with 36.7 million people in the last 50 years. The population growth rate was 2.2 between 2009 and 2019. The population shows the current and future demand for food. The country now grapples on ensuring sustainable availability and affordability of food to her citizens. Our food security faces many threats such as climate change, disease and pest infestations.
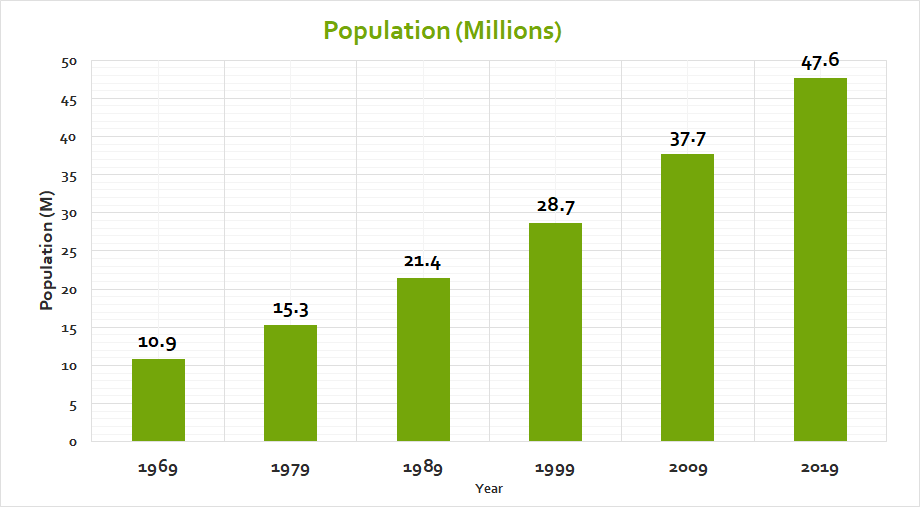
Population growth and urbanization lead to land subdivision into smaller parcels shrinking our arable land further stressing our yields.
Kenya surveys her households in a national census every ten years. The latest survey; Kenya Population and Housing Census (KPHC 2019) was in August 2019 by the Kenya National Bureau of Statists (KNBS).



