They say farming is risky and unpredictable… but as a smart farmer you do it profitably. In todays post, discover the the best business models that can turn your agriculture operations into a goldmine.
There are two types of farmers the smart rich farmers and others. The rich farmers do more than grow crops and raise animals. They invest in commercial production and marketing including aggregation, value addition and efficient distribution. They understand the benefits of planned investing in order to make more money. Smart farmers research, write and use business plans and strategic plans for shortterm and long term growth. Importantly they use use proven business models and to avoid business failure by mitigating risks.
What is a Business Model?
A business model is a strategic framework that defines how a company creates, delivers, and captures value in a sustainable and profitable way. It outlines the methods and processes a business employs to generate revenue, serve its customers, and manage expenses.
An agribusiness model defines how your agricultural enterprise create, deliver, and capture value across the agricultural value chain. It encompasses all activities from input supply, production, processing, marketing, and distribution to final consumption.
Components of an Agribusiness Models
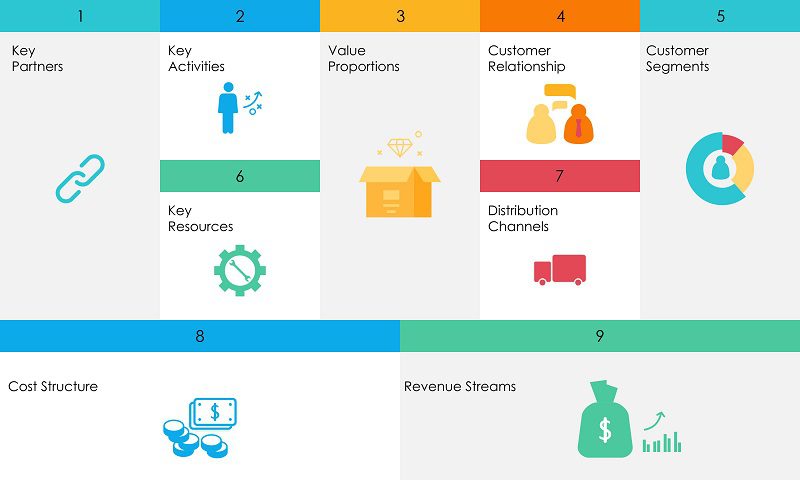
An agribusiness model consists of several key components. These include a value proposition (unique benefits offered), customer segments (target markets), revenue streams (ways to earn income), cost structure (expenses), key resources (necessary assets), key activities (critical tasks), key partnerships (collaborations), and distribution channels (how products reach customers).
The table below summarises these Component or the essential element of any agribusiness model. in addition you get a brief explanation of what the component entails and finally examples of 2025 Agribusiness Models in Kenya
| Agribusiness Component | Description | 2025 Agribusiness Models for Smallholders in Kenya |
| Value Proposition | The unique offering that sets the agribusiness apart, whether it’s a product, service, or technology. | Organic & Regenerative Farming (better prices), Drought-Resistant Crops, Fast-Maturing Livestock Breeds |
| Target Market | Who the farmers sell to—local consumers, traders, supermarkets, or export markets. | Direct-to-Consumer Sales (Social Media, WhatsApp groups), Contract Farming with Processors & Exporters, Community Supported Agriculture (CSA) |
| Revenue Streams | Ways to generate income beyond selling crop and livestock. | Agroprocessing (Making Flour, Oils, Dried Fruits), Agri-Tourism (Farm Visits, Eco-Tours), Selling Farm Inputs (Seeds, Organic Fertilizers) Farm Stays, Agri-Training & Consulting |
| Cost Structure | Key expenses such as seeds, labor, and equipment. | Cooperative Farming Models (cost-sharing), Agri-Fintech Loans & Crowdfunding |
| Key Activities | The daily operations needed to keep the business running profitably. | Vertical & Container Farming (Urban & Peri-Urban Farms), AgriTech Use (Mobile Apps for Weather, Market Prices), Cooperative Storage & Aggregation |
| Key Resources | Essential inputs like land, water, knowledge, and financing. | Crowdfunding & Mobile Money Loans (M-Pesa, Tala, FarmDrive), Solar-Powered Cold Storage, Agroforestry (Fruit Trees + Crops for Long-Term Income) |
| Partnerships | Collaborations that help smallholders scale up and reduce costs. | Village Savings & Loan Groups (Table Banking), Micro-Franchising with Agribusinesses, NGO & Gov’t Support Programs |
| Distribution Channels | How the agribusiness reaches customers, including online and offline channels. | Digital Marketplaces (Twiga Foods, Mkulima Young, Jumia Fresh), B2B Supply to Schools, Hospitals & Hotels, Local Cooperatives & Aggregators |
| Sustainability & Innovation | How smallholders ensure long-term success and adapt to change. | Regenerative Farming (Soil Health & Organic Practices), Carbon Credit Farming (Selling Carbon Offsets), Use of AI & Drones for Precision Farming |
Advantages of a using an Agribusiness Business Model
You need to start by developing a sound business model. Among other things, it will help you to define your vision (why you exist) and mission (how to achieve your goals). In addition, you will have following benefits;
- Guides your agribusiness in achieving profitability.
- Helps attract investors by demonstrating a clear plan for revenue generation.
- Enables you to adapt to market changes and innovate as needed
How to Select the Best Business model
In this section, learn how to select the best model for your farm or agribusiness. It gives you the 6 steps to use,
- Understand Your Goals and Drivers; Define your objectives, such as increasing profits, accessing markets, reducing risks, or adopting sustainable practices.
- Assess Your Resources; Evaluate your available land, labor, financial capital, equipment, and access to inputs like seeds and water.
- Analyze Market Opportunities; Research demand for crops or products you can produce and identify potential buyers or markets.
- Evaluate Risks and Financial Requirements; Consider the financial risks of scaling up and whether you can access credit, insurance, or partnerships to mitigate risks.
- Leverage Technology and Innovation; Explore agri-tech solutions like mobile apps for market prices, precision farming tools, or digital platforms for connecting with buyers.
- Consider Enabling Environments; Assess the policy environment, infrastructure (e.g., storage), and institutional support available in your region.
How to Use IBM customer centric Business model
The covered section is the business model. The article have used the customer-centric business model (magic triangle) by the BMI Labs. It has four components namely: Who: (target consumers) What: (value propositions) How: (value chain) Why: (revenue model) The post will discuss each of the parts in detail with examples.
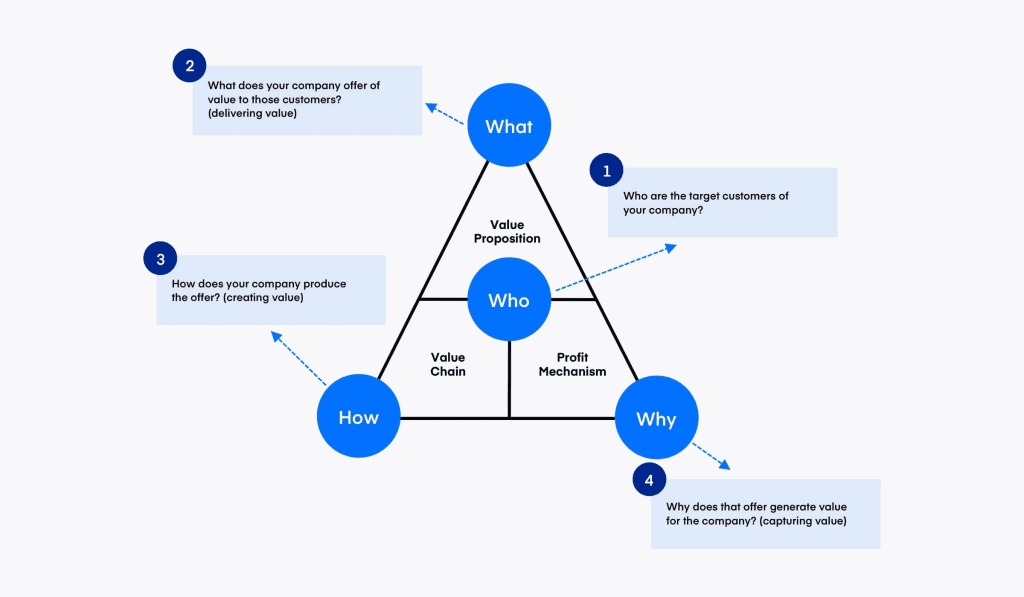
Who (Consumers)
The Who in the business model refers to the target customers of your wholesale or retail agribusiness. To get high profits target both the individual (B2C) consumers and other businesses (B2B) like consumers businesses like millers and dairy cooperatives.
To identify paying consumers, offer them high quality and affordable products and services. conduct simple market research to define their age, gender, income and location. An example of your farm’s niche market can be:
- Young unmarried people.
- Aged between 20-35 years.
- Living in the Nairobi Metropolitan.
- With an annual income of $36,000 and above.
- Who prefer non-meat products.
What (Value Proposition)
In the BMI lab business model, the what refers to value propositions, products and services your agribusiness will offer to your consumers. The traditional value proposition was to display your commodity in a farm shop and wait for walk-in customers. Today, grain, milk and meat traders offer various value propositions to edge out the competition. Examples you can try beyond the COVID-19 pandemic for extra profits are:
- Create place utility: Make free deliveries using cheap transport like motorbikes to reduce the cost of consumers taking trips to your shop.
- Aggregation and bulk breaking: collect small quantities into a large supply of cereals for institutional buyers like schools who buy in bulk. Or breakbulk by selling small quantities for individual consumers.
- Diversity & choice. offer a range of cereals, pulses, dried tubers and spices products under one roof.
How (Value Chain)
The third component in the business strategy model is the How or the value chain. It includes the operations you undertake like sourcing products from other small farmers and traders, transport, storage and packaging before sales. Your value chain must be efficient and its output of high quality.
Examples farmers can become rich by working on their how are:
- Direct sales to your buyers: it is costly to sell your goods using brokers. Instead, sell directly to your consumers. You may need an e-commerce site or mobile app for direct sales.
- Transport: Own your own transport or hire one together with other farmers to cut on costs of transport.
- Food processing: food processing or value addition is an ingenious way of making extra profits in the agriculture businesses. One cheap method is grain milling for cereal farmers. To diversify further, mill and package pure or blended maize, wheat and porridge flours.
- Diversify: sell a wide range of agriculture products instead of focusing on one product only. E.g your ranch can grow hay, sell pedigree bulls and steers and open a prime cuts butchery.
- Risk mitigation: Buy insurance premiums for your crops, livestock and business assets against climate and business risks like floods, fire and theft.
Why (Revenue Model)
The final component in the model is the why or your revenue model. It is how you will price, market, market, sell and collect payments or value from your customers. will you operate a physical or online shop. In terms of payments, will your farm store, dairy processor or butchery
An example for a modern vegetable fruits or eggs shop will be; use of free Social media sites like mobile Apps, Facebook and WhatsApp to market your cereal store to existing and new customers. They can view products, compare and order in advance and pay using mobile and internet banking like Mpesa. In turn, as a social distance measure against COVID-19 spread, dispatch their orders as parcels to their homes or pick up locations.
Examples of Best Business Models for Farmers in Kenya
The four popular agribusiness models for farmers in Kenya
- Contract Farming: Provides guaranteed markets and reduces price risks.
- Cooperatives: Farmers pool resources to access better markets and inputs.
- Agri-Tech Platforms: Use digital tools and mobile Apps to connect with buyers or optimize production.
- Family Farming with Diversification: Combines traditional practices with new crops or value-added processing.
Other emerging business models worth noting and exploring in 2025 include;
1. Precision Agriculture
Precision agriculture uses technology such as GPS, sensors, and data analytics to optimize farming practices. It enables farmers to monitor and manage crops with high precision, improving yields and reducing waste.
Companies like Climate FieldView and John Deere use data-driven platforms to provide insights on soil health, weather patterns, and crop performance
- Benefits:
- Increased efficiency in resource use (e.g., water, fertilizers).
- Reduced environmental impact.
- Enhanced crop productivity.
2. Vertical Farming
Vertical farming in Kenya involves growing crops in stacked layers within controlled environments. This model is ideal for urban areas where land is scarce.
AeroFarms utilizes vertical farming technology to grow pesticide-free greens year-round in urban settings
- Benefits:
- Maximizes space utilization.
- Reduces water usage by up to 95%.
- Enables local food production, reducing transportation costs.
3. Aquaculture Businesses
Focuses on the breeding, raising, and harvesting of aquatic organisms like fish and shellfish. It addresses the growing global demand for seafood while promoting sustainability. Other related businesses in Kenya include snail farming, spirulina Algae production, BSF Insect farming and Azolla farming
Companies like Mowi (Norway) lead in sustainable aquaculture practices by using innovative feed solutions and reducing environmental impacts
- Benefits:
- Provides a reliable protein source.
- Reduces pressure on wild fish stocks.
- Creates opportunities for coastal communities.
4. Organic Farming Ventures
Organic farming avoids synthetic chemicals, focusing on natural processes to grow crops and raise livestock to improve soil health and produce chemical-free food.
- Benefits:
- Meets consumer demand for healthier food options.
- Promotes biodiversity and ecosystem health.
- Commands premium prices in markets.
5. Agricultural Technology Startups
These startups integrate advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), robotics, and blockchain into agriculture.
Example: Startups like Indigo Agriculture use microbiology to improve crop resilience while others like FarmLead provide online grain marketplaces24.
- Benefits:
- Increases transparency in supply chains.
- Improves farm management through automation.
- Enhances access to markets for smallholder farmers.
6. Contract Farming
In this model, agribusinesses enter agreements with farmers to produce specific crops or livestock under agreed terms.
In Kenya, partnerships between sorghum producers and the breweries have improved market access for smallholders
- Benefits:
- Provides guaranteed markets for farmers.
- Reduces risks associated with price volatility.
- Encourages adoption of quality standards.
7. Platform-Based Agribusiness Models
Digital platforms connect farmers with buyers, suppliers, or financial services, enabling efficient transactions and information sharing.
Platforms like Full Harvest facilitate the sale of surplus or imperfect produce to reduce food waste
- Benefits:
- Expands market access for farmers.
- Reduces transaction costs.
- Promotes sustainability through waste reduction.
8. Smallholder-Focused Models
These models integrate small-scale farmers into larger value chains by providing access to inputs, training, and markets.
The World Bank’s projects in Latin America have successfully linked smallholders with buyers, increasing incomes by up to 30%.
- Benefits:
- Empowers rural communities.
- Enhances food security.
- Promotes inclusive economic growth.
In Conclusion
The best agribusiness model depends on your unique circumstances—your resources, goals, and market conditions. Start small by experimenting with low-risk models like contract farming or cooperatives before scaling up to more complex ones like joint ventures or vertical integration.



