Climate change is the worst risk to modern agriculture. Droughts, floods and erratic weather patterns have become more severe and frequent in the recent past. It impacts the food security, jobs and incomes of millions of farmers across the globe. Climate-smart agriculture or CSA can be a lasting solution to increase farm yields, enhance resilience and reduce emission of greenhouse gases (GHGs).
What is CSA?
According to FAO, the definition of CSA is “agriculture that sustainably increases productivity, enhances resilience (adaptation), reduces or removes GHGs (mitigation) where possible, and enhances the achievement of national food security and development goals”.
Benefits of climate-smart agriculture
CSA is one of the main tools of achieving various sustainable development goals (SDGs) like zero hunger, clean energy and no poverty. Its benefits to farmers, herders and fishermen can be drawn from its three pillars from the definition above. Besides, the consumers, governments and other value chain players in agriculture and food markets will enjoy these benefits.
- Increase yields: According to World bank, one of the outcomes of CSA is to produce more and better food to improve food and nutrition security and boost incomes for people in rural areas. In CSA, the increased productivity from crops, livestock and fish has no negative effect on the environment.
- Reduce vulnerability: According to CSA Guide, CSA will help farmers to adapt and improve their capacity to manage climate change risks like droughts, pests and diseases. In short and long term scenarios your resilience to bounce back after climate shocks like erratic weather is high.
- Reduce GHGs emissions: conventional agriculture is a leading cause of GHGs emissions that lead to global warming. CSA promotes farming methods that reduce or remove emissions from the atmosphere. These include reducing deforestation and desertification.
Methods of climate-smart agriculture
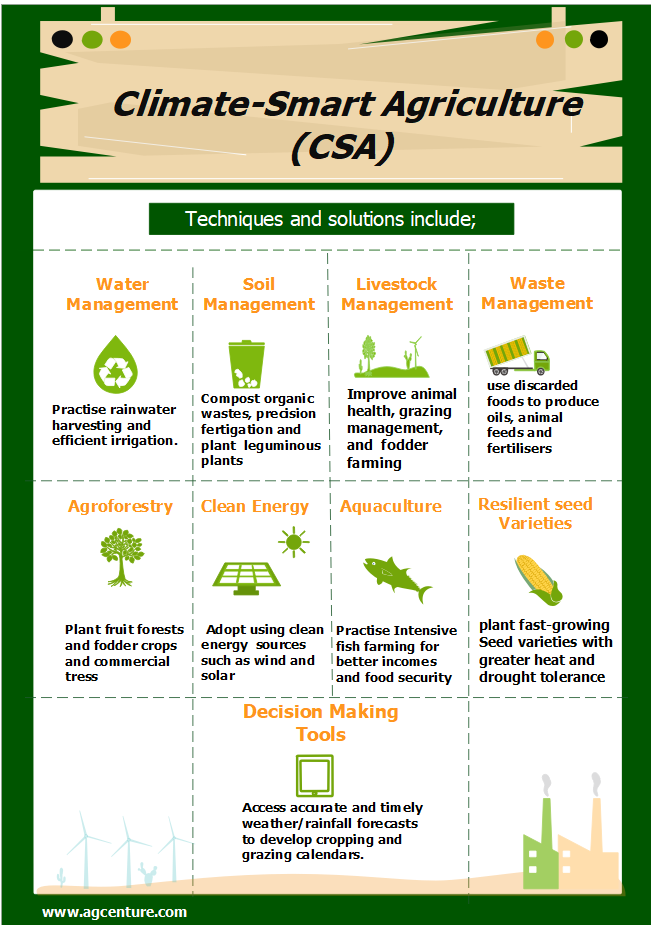
As illustrated, adopting CSA has many benefits. As a gardener, pastoralist or fisherman you can adopt it today. In this article, we look at methods, innovations or technologies in CSA that are easy to adopt. They include the use of resilient seed varieties, agroforestry and use of clean energy like solar.
Resilient seed varieties.
plant fast-growing seed varieties with great heat and drought tolerance. This CSA method will save you from partial or full crop failure from erratic weather patterns. In flood prone areas, use flood resilient seed varieties like rice, maize and sugarcane that are tolerant to excess soil moisture and are resilient to flood submergence. Other types of crop seed varieties or animal breeds are modified to be resilient to pests or tolerant to diseases.
Decision-making technologies.
CSA advocate for collection, analysis and use of accurate and timely data for farm decision making. An example is use of satellites to monitor and forecast weather or pests like desert locust’s migration patterns. These weather forecasts tools like the KAOP by KALRO in Kenya can help farmers to develop informed cropping and grazing calendars minimizing the investment risks. Others like mbegu choice, a seed bank database in Kenya and Uganda can help gardeners, ranchers and pastoralists to access their regional specific information like best seeds to plant in your agroecological zone.
Agroforestry
You will plant fruit forests, fodder trees and commercial trees to reduce soil erosion, earn carbon credits and conserve animal feed for your cattle. Agroforestry involves planting multi-purpose trees alongside other beneficial crops or in grazing fields. It will support your farm income through beekeeping, providing shade for your crops and animals and providing wind breakers that reduce soil erosion by wind. Forests will increase infiltration process in your area thus reducing floods among other benefits. Trees one can plant include moringa, tree lucerne and grevilia.
water management and use.

To enhance crop and livestock yields CSA promotes rainwater harvesting and efficient irrigation methods to capture, retain and use water effectively.
You can harvest rainwater from rooftops or flowing storm or flood waters. You may need to install underground and surface storage water tanks, reservoirs or water pans. You will use the cheap stored water for irrigation, watering animals and other farm activities in the dry months.
Efficient or precise irrigation methods reduce water wastage and soil erosion. They include use of sprinklers and drip irrigation kits for deliver water, fertilizers and chemicals to roots.
Aquaculture
In CSA fish farming, consider Intensive fish farming to improve the environment farmer incomes and food security for fishermen. Its main focus is to reduce wastage. Farming fish in ponds helps to control overexploitation of fish resources in water bodies.
clean and efficient energy use
Adopt clean or renewable energy sources like wind and solar for your farm needs like lighting, heating and cooling. The most affordable is installing photovoltaic solar panels to tap solar energy and convert it to electricity. For use at night, buy storage or the rechargeable batteries.
Livestock Management

CSA advocate for improved animal health, grazing management, livestock insurance and fodder farming amongst other methods. These will improve the resilience and incomes of ranchers and pastoral communities as follows: –
- Animal health: use crossbreeding, better nutrition and animal husbandry and responsible use of antibiotics and vaccination to improve and maintain good health of your farm animals.
- Grazing management: practice rotational grazing, herd management and planned timing, movement and grazing to conserve grasslands, enhance soil health and water retention in your ranch.
- Livestock insurance: use weather forecasts data and index-based livestock insurance to deal with weather risks. An example is the Kenya Livestock Insurance Program (KLIP). Herders are subsidized to pay premiums, in case of trigger event, they receive money to buy water and fodder that maintain the quality of animal health.
- Pasture management and nutrition: improve quality of pasture including agroforestry and commercial fodder farming through fertigation and irrigation. You will harvest fodder during wet season and store it in silage and other means for use as animal feed and fodder in dry periods. These will give you equal milk and meat quality in wet and dry season.
Read Next: What is Sustainable Agriculture ?
soil management
CSA methods for managing soil health are composting organic wastes, precision fertigation and planting leguminous cover crops for mulching and nitrogen fixation. Other methods include rangeland management and agroforestry.
waste management
Practice responsible waste management to reduce solid and water waste reduction and reduced air emissions of GHGs. An example is manure management by composting, covering manure heaps and responsible application. In markets and farms, you can use the discarded food wastes to produce oils, animal feed and organic fertilizers.



