Do you fear GMO food? Whether you’re pro or anti-genetically modified organisms (GMOs) crops, there are many unknowns about this biotechnology innovation.
Farming and trade of GMO crops and products will increase the food supply for human and livestock consumption in Kenya. It will do this by solving major challenges facing agriculture in Kenya such as pests and diseases. On the other hand, there are some known and unknown health, environmental, and socioeconomic risks and concerns of handling GMOs.
In this explainer post, you will learn all you need to know about GMO Crops in Kenya.
What is GMO
Genetically modified organisms (GMOs) are organisms whose genetic makeup has been altered or enhanced to achieve a particular purpose or use. The major aims are four;
- Change product characteristics, e.g. make products more durable.
- Improve plant resistance to pests and pathogens.
- Enhance the productivity of organisms.
- Increase nutritional value, such as Vitamin A content in foods
Read Next: How to choose the best planting seeds for your farm
The major aim for their adoption in farming and trade is thus to improve farmers’ yields and income despite the vagaries of weather and pests. The list below are some GM Crops in Kenya and their targeted traits
| CROP | GM TRAIT |
|---|---|
| Maize | Insect resistance, drought tolerant, nitrogen efficient |
| Cotton | Insect resistance, herbicide tolerant |
| Cassava | Insect resistance, herbicide-tolerant |
| Banana | Disease resistant |
| Sorghum | Nutritionally enhanced |
| Sweet Potato | Virus resistant, weevil resistant |
| Pigeon Pea | Insect resistance |
How are GMO Crops Modified?
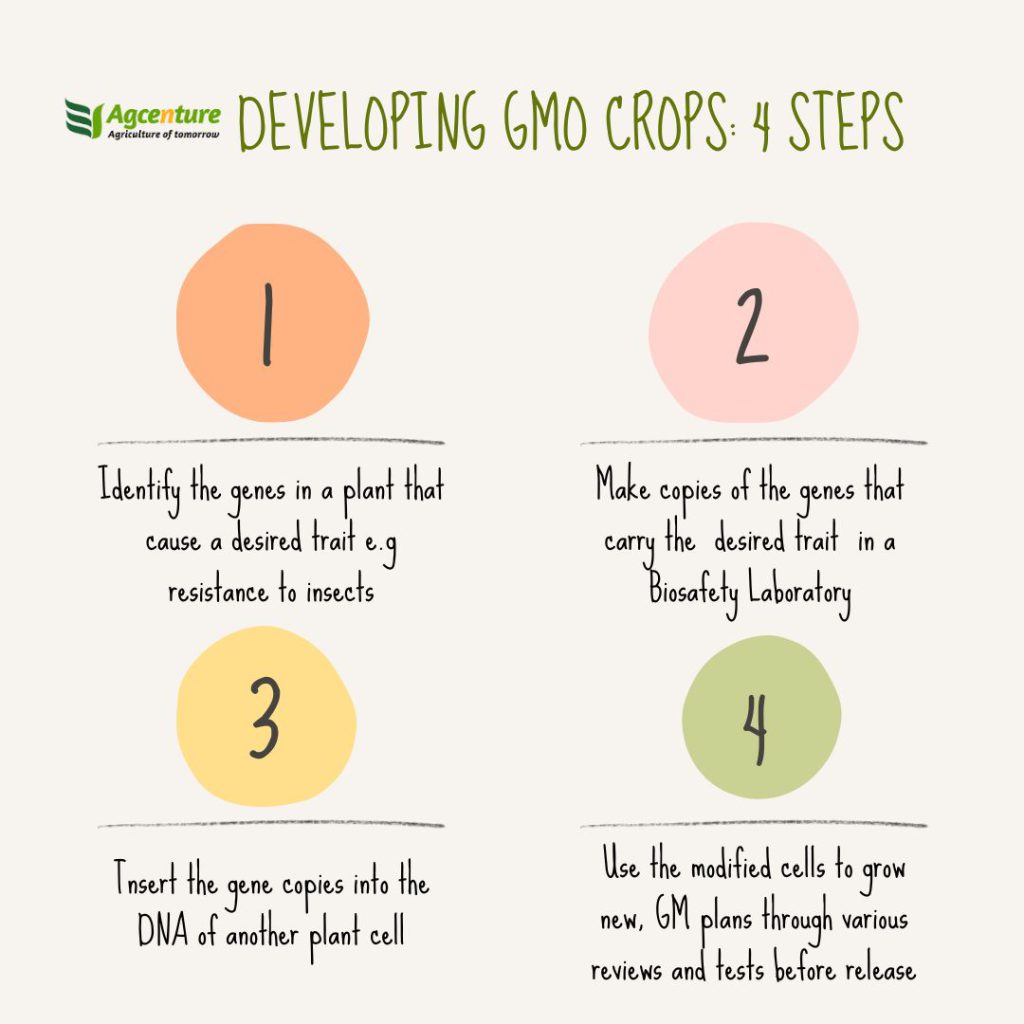
The process of developing and releasing GM crops is complex, expensive, and long. The regulations may vary from one country to another. In Kenya, the biotechnology processes of research and approval before the environmental release and commercialization are overseen by the National Biosafety Authority. They have the mandate to oversee the execution of the biosafety (environmental release) regulations that were published in August 2011. It covers all aspects and activities used to release of GMOs into the environment; placing them on the market and their trade.
The regulations were designed to address potential adverse effects of genetically modified organisms, to protect human health and the environment when conducting environmental release tests, and to avail GM products for use by the public. The regulations can be simplified into a 4 steps process. These may take between 10-15 years
What GMO Crops are Currently grown in Kenya?
Since 2019, the government approved the growing of BT GM cotton. Since it is a nonfood crop, it was considered to have lower implications on human health.
There are other GM food crops now undergoing trials in Kenya. They include maize, cassava, sweet potato, Irish potato, sorghum, and banana. Elsewhere, there are GM varieties of soybean, canola, potatoes, eggplant, strawberries, corn, tomatoes, lettuce, cantaloupe carrots, etc. In the future, Kenya may venture into those and others such as medicines, vaccines, foods, food ingredients, feeds, and fibers
GMO foods were first approved for human consumption in the United States in 1994. By the year 2020, the GM crops for Soybeans, cotton, and corn in the US were as follows;
| GM Crop | Portion planted | Top uses |
|---|---|---|
| GMO Soybeans | 94% | Used for poultry and livestock feeds Making soybean oil. Ingredients in processed foods |
| GMO Cotton | 96% | Source of cotton in the textile industry Used to make cottonseed oil Cottonseed meal and hulls are also used in animal feed |
| GMO Corn | 92% | Used to make processed foods and drinks Used to feed livestock, like cows, and poultry, |
Pros and cons associated with GMOs
What are the benefits of genetically modified crops? The key reasons for farming GM crops are to achieve higher crop yields, and income and enhance people’s health cheaply. On the other hand, there are many ethical, unintended, and unknown consequences according to anti-GM lobby groups. In this post, we give you both the pros and cons of GM Crops.
Pros of Farming and Using GMOs
On average, GM technology has increased crop yields by 21%. There are many more benefits of growing GMOs. These can range from fast growth to resistance, and tolerance.
Some of the other benefits include;
GMOs use fewer pesticides
According to a recent study, GMO farmers have reduced pesticides used by over 8.3 % between 1996 and 2018.
GMO crops have been altered to withstand some insects, weeds, or pests. An example is the BT corn or BT cotton. They are coded with Bacillus thuringiensis, a naturally occurring soil bacteria. This bacterium has protein that protects the crop from many pest attacks thus reducing the need to spray them with pesticides.
Apart from lowering your cost of growing food, it helps you reduce your carbon footprint.
GMOs are cheaper to grow and buy
Do you know GMO foods such as corn, beets, and soybeans are 15-30% cheaper?
GMOs are designed to withstand the worst vagaries of weather or pests. As such, a farmer will get the same harvests using fewer pesticides, water, or land. By a farmer saving on the cost of production, he can lower the price of food.
GMOs are more nutritious
Some GMO crops such as sorghum, maize, and Irish potatoes are genetically engineered to add vitamins and minerals.
As such eating GMOs will enjoy more nutrients compared to conventional crops. These can alleviate millions of people suffering from hunger and malnutrition in some of the harshest climates and soils to support crop farming.
GMOs are more Profitable
Food growers and traders earn higher profits from GMOs than from conventional crops. The following are what makes GMOs sell better and easier;
- Increased attractiveness and appearance to consumers, for example, apples and potatoes that are less likely to bruise or turn brown
- Enhanced flavor and nutrients
- Fast-maturing plants and animals.
- Longer shelf life, less food waste thus increasing food security
- Easy to preserve and transport them.
Cons of Growing and Eating GMOs
There are many risks and controversies surrounding the use of GMOs. These unknown consequences come from altering the natural state of an organism. The key cons are associated with unintended impact on other species, unintended economic consequences, and also philosophical or religious concerns including associating GMOs with increased incidences of cancer cases. The specific disadvantages of growing GM Crops are;
Economic Consequences
The seed cost for GM crops is more expensive than non-GM crops. You will also need to procure certified seed each season. Even if this sounds challenging, GMO crops lower the costs of production by reducing inputs of machinery, fuel, and chemical pesticides
Allergic reactions
Some newly modified GMO food crops such as Soya or Nuts can carry an allergen from the foreign gene from the other crop or bacteria.
Cancer Risk
Some concern about eating GMO foods is that they can contribute to the development of cancer.
They do this by raising levels of potentially carcinogenic substances in the body. However, according to the American Cancer Society, there is no proven evidence that currently available GMO foods either increase or reduce the risk of cancer.
Unintended Environmental Concerns
There are many environmental concerns about replacing conventional crops with GMO crops. These may include;
- Outcrossing: where genes from GMO foods pass into wild plants and other food crops
- Resistance: Some evidence points to the possibility of creating more weeds or harder-to-kill invasive pest species
- Biodiversity concerns: Adoption of GMO crops may lead to a reduction in insect biodiversity when crops are resistant to insects
- Nutrition: GMO crops can have foods that are less nutritious than the original crop.
Fear of the unknown
There is little gathered evidence of GMO organisms on humans in the long term.
In addition, there are many unanticipated effects of GMOs effects on other crops or animals stemming from the unintended transfer of genes from one GMo plant or animal to another plant, human, or animal not intended for genetic modification.
To Grow or Not to Grow GMOs in Kenya?
As the post and research demonstrate, GMOs can benefit Kenya’s food security. This can stem from an increase in the availability and quality of food, medical care, and a cleaner environment. Other benefits are an improvement in economic growth and development from increased domestic and international trade. Finally, GM foods have the potential to alleviate hunger and diseases not only in the region but worldwide.
Read Next; How to select the best seeds for your farm
On the other hand, Eliminating GMOs would lead to higher food prices, a significant boost in greenhouse gas emissions due to land use change, and a major loss of forest and pasture land
GMOs’ full potential cannot be fully realized without due diligence and thorough attention to the risks associated with each new GMO on a case-by-case basis. In addition, there is a need to review GMO regulations and empower authorities and agencies mandated to execute them.




Stop GMO foods it Wii kill us